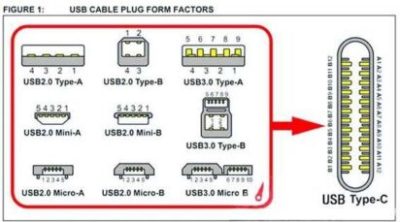
What is a USB interface? The function and fabrication of precision USB interfaces.
Universal Serial Bus (English: Universal Serial Bus, abbreviation: USB) is a serial bus standard and a technical specification for input and output interfaces. It is widely used in information and communication products such as personal computers and mobile devices, and has been extended to other related fields such as photographic equipment, digital TV (set-top boxes), and game consoles. The latest generation is USB4, with a transmission speed of 40Gbit/s, a three-stage voltage of 5V/12V/20V, and a maximum power supply of 100W. The new Type C interface allows positive and negative blind insertion.
How the USB interface works
USB is an external bus standard that regulates the connection and communication between computers and external devices. The USB interface has a hot-swap function. The USB interface can connect a variety of peripherals, such as mouse and keyboard. USB was jointly launched by Intel and other companies in 1996 at the end of 1994. It has successfully replaced serial ports and parallel ports, and has become a must-have interface for computers and a large number of smart devices today. The USB version has gone through years of development and has now developed into the USB4 version. For most engineers, the main obstacles to developing USB2.0 interface products are:
To face the complex USB2.0 protocol, write the driver of the USB device by yourself, and be familiar with the programming of the single-chip microcomputer. This not only requires considerable experience in VC programming, but also the ability to write hardware (firmware) programs for USB interfaces. So most people give up developing USB products by themselves.
The development history of USB interface
USB 1.0
USB 1.0 appeared in 1996, with a speed of only 1.5Mb/s (bit per second); it was upgraded to USB 1.1 in 1998, and the speed was greatly increased to 12Mb/s. This standard interface can still be seen on some old devices. USB1.1 is a relatively common USB specification, and its high-speed transmission rate is 12Mbps. The transmission rate of the low-speed mode is 1.5Mbps (b means Bit), b/s generally indicates the bit transmission speed, and bps indicates the bit transmission rate, which are equal in value. B/s and b/s, BPS (bytes per second) and bps (bits per second) should not be confused. 1MB/s (megabyte/second) = 8Mbps (megabit/second), 12Mbps = 1.5MB/s, most MP3s are of this type of interface.
USB 2.0
The USB2.0 specification evolved from the USB1.1 specification. Its transmission rate has reached 480Mbps, converted to MB is 60MB/s, enough to meet the rate requirements of most peripherals. The “Enhanced Host Controller Interface” (EHCI) in USB 2.0 defines an architecture compatible with USB 1.1. It can drive USB 1.1 devices with USB 2.0 drivers. In other words, all devices that support USB 1.1 can be used directly on the USB 2.0 interface without worrying about compatibility issues. And accessories like USB cables, plugs, etc. can also be used directly.
The change brought about by the use of USB for printer applications is a substantial increase in speed. The USB interface provides a connection speed of 12Mbps, which is more than 10 times faster than the parallel port. At this speed, print file transfer times are greatly reduced. The USB 2.0 standard further increases the interface speed to 480Mbps, which is 20 times the speed of ordinary USB, and greatly reduces the transmission time of printing files.
USB 3.0
The USB 3.0 Promoter Group is composed of industry giants such as Intel, Microsoft, Hewlett-Packard, Texas Instruments, NEC, and ST-NXP. The next-generation USB 3.0 standard that the organization is responsible for formulating has been officially completed and released publicly. The theoretical speed of USB 3.0 is 5.0Gb/s, but in fact it can only reach 50% of the theoretical value, which is close to 10 times that of USB 2.0. The physical layer of USB3.0 adopts 8b/10b encoding method. The theoretical speed calculated in this way is only 4Gb/s, and the actual speed has to deduct the protocol overhead, which is less on the basis of 4Gb/s. Can be widely used in PC peripherals and consumer electronics.
USB 3.0 will be called “USB SuperSpeed” in actual device applications, following the previous USB 1.1 FullSpeed and USB 2.0 HighSpeed. Commercial controllers supporting the new specification are expected to be available in the second half of 2009, and consumer products are already on the market.
USB 3.1
USB 3.1 Gen2 is the latest USB specification, which was initiated by companies such as Intel. The data transmission speed can be increased to a speed of 10Gbps. Compared with USB 3.0 (ie USB 3.1 Gen1) technology, the new USB technology uses a more efficient data encoding system and provides more than double the effective data transfer rate. It is fully backward compatible with existing USB connectors and cables.
USB 3.1 Gen2 compatible: existing USB 3.0 (ie USB 3.1 Gen1) software stack and device protocol, 5Gbps hubs and devices, and USB 2.0 products.
USB-IF’s latest USB naming convention, the original USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 will no longer be named, and all USB standards will be called USB 3.2. Considering compatibility, USB 3.0 to USB 3.2 are called USB 3.2 Gen 1, USB 3.2 Gen 2, and USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 respectively.
USB 4.0
The USB4.0 specification was published by the USB Implementers Forum on August 29, 2019. USB4 is based on the Thunderbolt 3 protocol. It supports 40 Gbit/s throughput, is Thunderbolt 3 compliant, and is backward compatible with USB 3.2 and USB 2.0.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά עברית
עברית Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latīna
Latīna Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt