Categorías de Producto
Etiquetas de productos
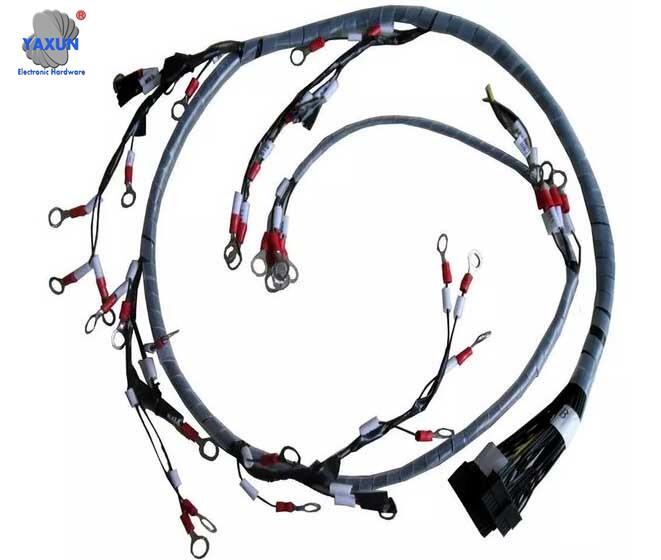
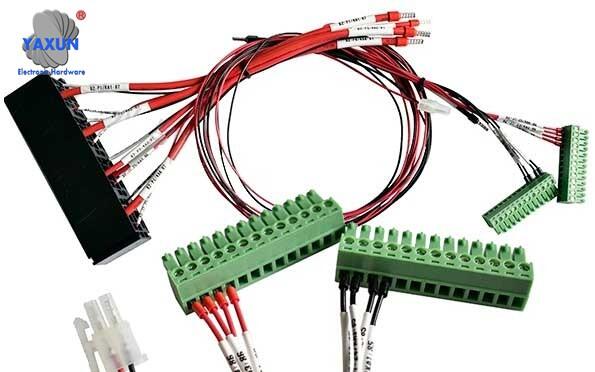
Juego de arnés de cableado asistido por robot para automatización
El flujo del proceso para fabricar mazos de cables para robots normalmente incluye los siguientes pasos:
Diseño y planificación: Diseñar el diseño, métodos de conexión y características eléctricas del mazo de cables según las necesidades y requisitos funcionales del robot. Considere factores como el área de la sección transversal del cable., longitud, codificación de colores y número de conductores.
Preparación de materiales: Seleccione cables de alta calidad, conectores, fundas protectoras y otros accesorios adecuados para aplicaciones robóticas. Asegúrese de que los materiales cumplan con los estándares y especificaciones relevantes de la industria..
Arnés de robot personalizado de acuerdo con sus requisitos de dibujo o muestra.
Cable: UL1015, UL1007;
Conector: Terminal tubular KT, terminal de primavera;
Campos de aplicación: Robots de barrido, robots de brazo mecánico, robots industriales, etc.;
Nombre: Arnés de alambre de robot; Tecnología de procesamiento: fascinante, ensamblaje y moldura;
Personalizado según las necesidades del cliente: longitud del arnés de alambre, especificaciones, color, etc.;
Exterior del mazo de alambre: tubería de retiro del calor;
Cable: UL1015, UL1007;
Voltaje de soporte: DC300V, 10 milisegundos;
Conector: Terminal tubular KT, terminal de primavera;
En resistencia: ≤2 ohmios;
Grado impermeable: IP67;
Resistencia a aislamiento: ≥10 megohm;
Ciclo de enchufe y desconocido: ≥5000 veces;
Prueba de spray de sal: ≥48 horas;
Áreas de aplicación: Robots de barrido, robots de brazo mecánico, robots industriales, etc..
Los cables de la cadena de arrastre del arnés de alambre de robot son principalmente adecuados para ocasiones con movimiento frecuente y flexión. Porque los cables más ordinarios deberían tener: alta flexibilidad, resistencia al aceite, Resistencia del agua poco profunda, resistencia a la humedad, Resistencia a los rayos UV, Excelente resistencia al clima, resistencia a baja temperatura, resistencia al desgaste, y la capacidad de soportar fuertes fuerzas mecánicas externas. El cable tiene una aceleración más rápida y una resistencia de flexión más fuerte que los cables flexibles ordinarios.
El arnés de alambre del robot tiene características como la alta resistencia a la torsión. Se enruta inteligentemente entre los brazos robóticos curvos y puede soportar una gran cantidad de curvas., que aumenta enormemente la vida útil del equipo.
Certificación de producto: Ul, IPC620, IP67, ALCANZAR, ROHS2.0, MASAS
Honores y calificaciones de la empresa.: Enterprise nacional de alta tecnología, Ul, IPC620, ISO 9001, ISO14000, ISO13485, IAF16949, etc..
El arnés de cableado del robot se refiere al sistema de arnés de cable y cableado utilizado para conectar varias piezas y componentes del robot. Incluye múltiples cables, conectores, mangas protectores y otros accesorios utilizados para transmitir energía, señales y datos para lograr el movimiento de robots, control y comunicación.
El flujo del proceso para fabricar mazos de cables para robots normalmente incluye los siguientes pasos:
Diseño y planificación: Diseñar el diseño, métodos de conexión y características eléctricas del mazo de cables según las necesidades y requisitos funcionales del robot. Considere factores como el área de la sección transversal del cable., longitud, codificación de colores y número de conductores.
Preparación de materiales: Seleccione cables de alta calidad, conectores, fundas protectoras y otros accesorios adecuados para aplicaciones robóticas. Asegúrese de que los materiales cumplan con los estándares y especificaciones relevantes de la industria..
Procesamiento de cables: Según los requisitos de diseño, Los cables están pelados, cortado y soldado. Asegúrese de que los extremos del cable tengan un buen contacto eléctrico y aislamiento del alambre.
Ensamblaje del conector: Inserte el cable en el conector, y ensamblar y fijar el conector. Asegure un buen contacto y una conexión estable entre el conector y el cable.
Instalación de manga: Coloque mangas protectores o vainas sobre arneses de cables para proporcionar protección física y blindaje electromagnético de los cables. Asegúrese de que el arnés de alambre sea suficientemente flexible y resistente a la abrasión.
Inspección de calidad: Inspección y prueba de calidad estricta de arneses de cables fabricados, incluyendo pruebas de conectividad de cable, prueba de aislamiento, Prueba de parámetros eléctricos, etc.. Asegúrese de que el arnés de cableado cumpla con los requisitos de diseño y los estándares relevantes.
Etiquetado y embalaje: Etiquetar y empaquetar el arnés de cableado para una fácil instalación y uso. La identificación generalmente incluye información como la función del conductor, codificación de colores, y longitud.
Instalación del arnés de cableado del robot

Arnés de cableado del robot de brazo mecánico
Las características de los arneses robóticos incluyen:
Complejidad: Los arneses de cableado robótico a menudo contienen grandes cantidades de cables y conectores utilizados para transportar múltiples tipos de energía, señales y datos. El diseño y la conexión del arnés de cable deben diseñarse con precisión en función de la estructura y función del robot.
Flexibilidad: El arnés del robot debe ser lo suficientemente flexible y flexible como para adaptarse al movimiento y los cambios de postura del robot durante el trabajo. El diseño y la selección de material del arnés deben tener en cuenta los requisitos de libertad y espacio de trabajo del robot.
Durabilidad: Los arneses de cableado robótico a menudo se someten a movimiento repetido y vibración durante largos períodos de tiempo, Por lo tanto, necesitan tener una buena durabilidad y resistencia al desgaste. La selección de materiales de arnés de cables y métodos de conexión debe poder resistir los requisitos del entorno de trabajo del robot.
Blindaje electromagnético: Dado que puede existir interferencia electromagnética durante la operación del robot, El arnés de cableado debe tener una cierta capacidad de blindaje electromagnético para evitar que la interferencia afecte la transmisión de la señal y el rendimiento del sistema.
Seguridad: Los arneses de cableado de los robots deben cumplir con los estándares de seguridad relevantes y los requisitos reglamentarios para garantizar la seguridad del arnés de cableado. Los arneses de cableado deben someterse a una rigurosa inspección y prueba de calidad para evitar posibles problemas eléctricos y fallas.
El proceso de fabricación y las características del arnés del robot le permiten proporcionar una potencia confiable, transmisión de señal y datos, admitir un control preciso y un funcionamiento eficiente del robot. Los procesos precisos de diseño y fabricación garantizan la estabilidad y confiabilidad del arnés de cables, mejorando así la eficiencia laboral y el rendimiento del robot.
Contáctenos
Esperando tu email, le responderemos dentro de 12 horas con la valiosa información que necesitabas.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά עברית
עברית Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latīna
Latīna Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt